What Stomach Pain After Eating Could Mean? Is It A Serious Issue?
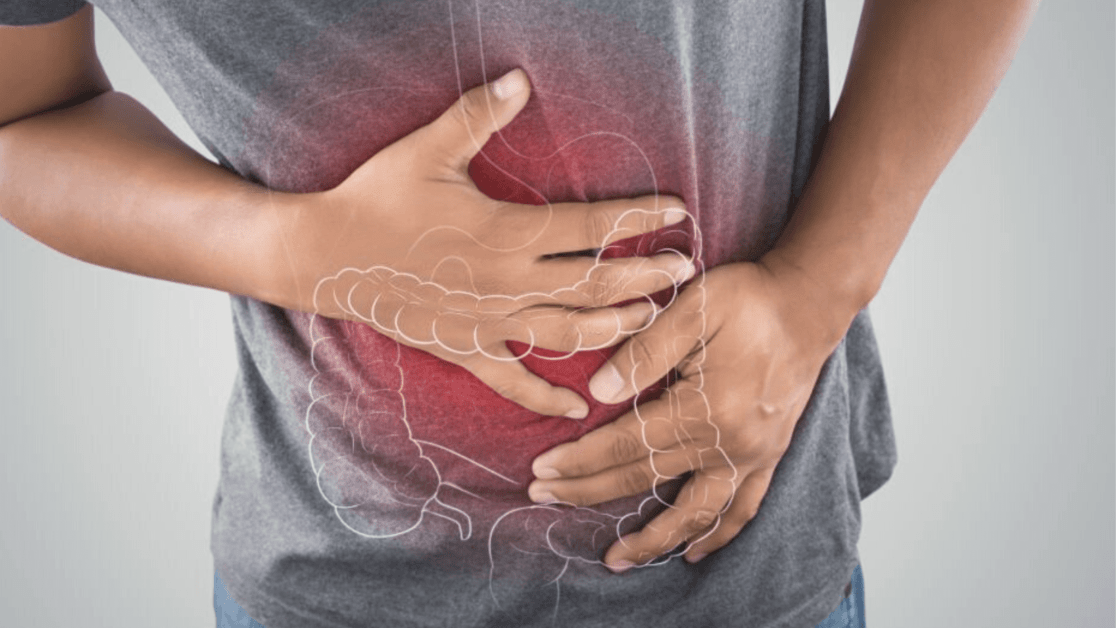
Many different conditions can cause stomach pain. It could indicate that there is a problem in your digestive system, like an ulcer or a gallbladder problem. Stomach pain can also be caused by other factors such as stress, anxiety, and too much gas in your stomach.
Stomach Pain: Home Remedies, Food To Avoid, And When To A Doctor?
If you have had the same stomach pain for a while, it might be time to see a physician. Stomach pain is often referred to as upper abdominal pain. It can also include pain in the lower right side of the abdomen. The cause of this type of pain can vary depending on what is going on in your body.
Heartburn is typically associated with this type of abdominal pain and can cause symptoms such as nausea and vomiting after eating. This type of abdominal pain is often caused by acid reflux from a problem with the esophageal sphincter muscle or from scarring after surgery on the esophagus.
Diarrhea, constipation, and rectal bleeding are also common causes of stomach pain. These symptoms may be accompanied by other signs such as weight loss, blood in the stool, and fever.

What Does Stomach Pain After Eating Mean?
There are various reasons why you may experience stomach pain after eating, and it can be difficult to determine which is the cause. The fact that you’re experiencing pain indicates that there’s something going on—whether it’s a simple case of indigestion or a potentially more serious condition. It is important to determine what the pain is causing so that you can receive treatment for it.
Indigestion, also known as dyspepsia, occurs when acids in your stomach digest food, causing your stomach lining to produce extra mucus. This can lead to symptoms such as burning sensations, stomachache, abdominal cramping, bloating, and nausea. As many as one-third of people in the U.S. experience indigestion at least once in their life. And while most cases resolve over time without treatment, some become more serious conditions requiring medical intervention.
Another possible cause of this type of abdominal pain is gallstones, pebble-shaped deposits in the gallbladder—a sac underneath your liver that helps store bile and releases it when you eat fat-containing foods such as eggs and meat—making them important for digestion. Gallstones can cause intense abdominal pains due to blockages or chemical imbalances in the gallbladder. If you have gallstones, they can cause severe abdominal pain that may last anywhere from a few hours to several days.
Possible Causes Of Stomach Pain After Eating
If you find yourself suffering from stomach pain after eating, there are several potential causes. The first and most likely culprit is simply overeating. It’s easy to forget when you’re enjoying a meal that your stomach is only so big and can only hold so much food at once. If this is the cause, the solution is simple: slow down while you eat, and don’t go back for seconds or thirds unless you’re sure you have room in your stomach for it.
In addition to overdosing on food, there could be something wrong with the food itself that’s giving you an upset stomach. You may have eaten something spoiled or undercooked, such as an uncooked vegetable or a rare steak.
Some people also have trouble with constipation and may feel a stomach ache due to not having gone to the bathroom recently enough—while it’s not always the case for everyone, cutting out certain foods like carbonated drinks and alcohol can help people who suffer from constipation feel better. If you’re worried about something specific that you’ve eaten but haven’t had any luck pinpointing what caused your symptoms, check in with your doctor.
When To See A Doctor About Stomach Pain?
Pain after eating, also called postprandial pain, is a common problem. It’s usually caused by gas and may be relieved by burping or passing gas.

You may have a more serious condition if these measures don’t work.
Call Your Doctor If You Have:
1. Signs that your food is stuck in your esophagus, such as coughing, gagging, chest pain, or trouble swallowing (dysphagia)
2. Indigestion that lasts longer than two hours after eating (heartburn)
3. Sudden onset of severe abdominal pain that comes on during or shortly after eating
Home Remedies For Stomach Pain
Here are some home remedies for stomach pain.
Home Remedies
1. Ginger is a natural anti-inflammatory that can help relieve symptoms of gastritis and inflammation of the stomach lining. You can take ginger in capsule form or drink ginger tea.
2. Aloe vera juice helps heal ulcers and other stomach problems-However, it should be used only under medical supervision as it can interact with blood thinners and cause other side effects if taken improperly (source).
3. Turmeric is yet another wonder herb that has been used for centuries to treat various illnesses and disorders. It contains curcuminoids, which have anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce inflammation in your digestive tract (source). You can take turmeric supplements or eat foods that contain turmeric, like curry powder or mustard seeds (source).
4. Peppermint oil helps soothe an irritated digestive tract by relieving bloating, cramping, and nausea caused by indigestion (source). Peppermint oil is available in many forms, such as capsules or drops, but we recommend using it topically on your belly instead of taking it orally because ingesting peppermint oil can cause heartburn and upset stomach, and diarrhea (source).
5. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that live in your gut and help with digestion by making it easier for your body to absorb nutrients from food (source). They also help reduce inflammation in your digestive tract, relieving symptoms of IBS (source).
Foods To Avoid If You Have Stomach Pain:
Here are four foods to avoid if you have stomach pain after eating:
Fatty or greasy foods: These include fried or fatty meats and high-fat dairy products like cheese and butter.
Spicy foods: Spicy meals tend to irritate the lining of the stomach, which can lead to heartburn or reflux.
Chocolate and caffeine: Chocolate contains a chemical called caffeine that stimulates the digestive tract and may trigger acid production in some people. Caffeine also increases gastric acid secretion, so it’s best not to drink coffee or other caffeinated beverages when suffering from heartburn or indigestion.
Alcoholic beverages: include beer, wine, hard liquor, and champagne (unless you are using them medicinally). Alcoholic drinks are digested quickly by the body and contain an enzyme that breaks down starch into simple sugars. This makes it easier for food particles to become trapped in the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) valve between your esophagus and stomach.
Foods To Eat If You Have Stomach Pain:
There are many foods that can help with stomach pain. These include:
Bananas: These fruits have high fiber content and are easy to digest. They also add bulk to the intestines, which helps to relieve constipation caused by irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Chamomile tea: This herbal tea is known to help relieve bloating and flatulence. It also has mild sedative properties that can help you relax and sleep well.
Cinnamon: Add this spice to your food or as a supplement to reduce inflammation in your digestive tract. It also helps lower blood sugar levels, which may be helpful for people with diabetes-related stomach pain.
Conclusion
In conclusion, there are several medical conditions that can cause stomach pain after eating. These include stomach ulcers, gastritis, and heartburn. The symptoms may vary, but they can become so severe that the patient must see their doctor to address them. Future research is needed to identify additional symptoms that can be presented by these problems and to better determine who might be at risk of developing them.
Dr. Edward Zelman
Dr. Edward Zelman works as a Neurologist with the expertise of over 15 years, helping more than thousands to get back in complete health through his research-proven treatments. He earned his Masters from Harvard University and completed his Ph.D. from Columbia University. Dr. Edward Zelman is one of the notable names in the medical industry for his work in pain management, chronic disorder, and so on. He is also a former faculty at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). At present, Dr. Edward Zelman is researching safe and effective natural remedies that can restore as well as maintain the youthful functioning of the body.
View All By Dr. Edward





![Relief Factor Reviews – Can This Formula Help To Reduce Inflammation? [Legit or Not!]](jpg/relief-factor-reviews-scaledc2a4.jpg)
